| [Java] JDK与Spring国际化支持 | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › jdk参数 -XX:LargePageSizeInBytes › [Java] JDK与Spring国际化支持 |
[Java] JDK与Spring国际化支持
|
0 序言
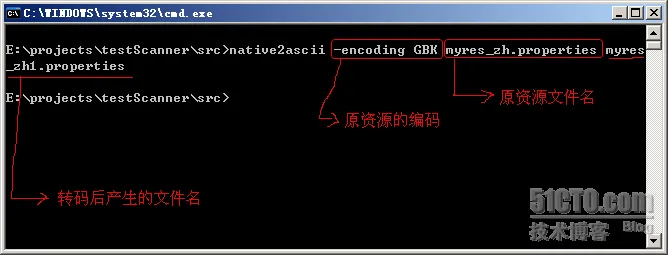
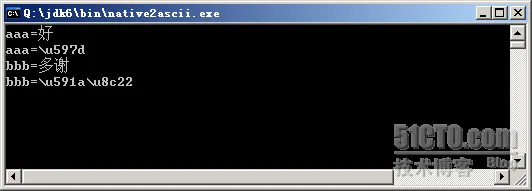
在Spring context 与Spring IoC对ApplicationContext以及Context相关的设计模式进行了介绍。 ApplicationContext作为一个Context在应用的运行层提供了IoC容器、事件、国际化等功能接口。 Spring的国际化(i18n)功能是通过MessageSource接口实现的,他提供了MessageSource::getMessage方法从预设的资源中获取对应的数据。 1 JDK 国际化核心组件 : Java 标准资源绑定 1.1 java.util.ResourceBundle 1.1.1 概述在介绍MessageSource之前,得先说清楚Java(J2SE)对国际化的基本实现——ResourceBundle,因为MessageSource是用它实现的。 ResourceBundle很好理解,他就是按照规范的格式放置*.properties资源文件,然后根据输入的语言环境来返回资源。 ResourceBundle类提供了软件国际化的捷径。通过此类,可以使您所编写的程序可以: 轻松地本地化或翻译成不同的语言 一次处理多个语言环境 以后可以轻松地进行修改,支持更多的语言环境说的简单点,这个类的作用就是读取资源属性文件(properties),然后根据.properties文件的名称信息(本地化信息),匹配当前系统的国别语言信息(也可以程序指定),然后获取相应的properties文件的内容。 使用这个类,要注意的一点是,这个properties文件的名字是有规范的:一般的命名规范是: 自定义名_语言代码_国别代码.properties 如果是默认的,直接写为:自定义名.properties 比如: myres_en_US.properties myres_zh_CN.properties myres.properties当在中文操作系统下,如果myres_zh_CN.properties、myres.properties两个文件都存在,则优先会使用myres_zh_CN.properties,当myres_zh_CN.properties不存在时候,会使用默认的myres.properties。 没有提供语言和地区的资源文件是系统默认的资源文件。 资源文件都必须是ISO-8859-1编码。 因此,对于所有非西方语系的处理,都必须先将之转换为Java Unicode Escape格式。转换方法是通过JDK自带的工具native2ascii. 1.1.2 示例1 Step1 我们有3个资源文件放置在classpath的根目录(本例是放在src/main/resource)中,文件名分别为: i18n_en_US.properties i18n_zh_CN.properties i18n_web_BASE64.properties文件中的内容如下: #i18n_en_US.properties say=Hallo world! #i18n_zh_CN.properties say=\u5927\u5BB6\u597D\uFF01 #i18n_web_BASE64.properties say=+-+-+-ABC Step2 然后,我们通过ResourceBundle类来使用这些i18n的资源文件: public class I18nApp { public static void main(String[] args) { //使用当前操作系统的语言环境 ResourceBundle rb = ResourceBundle.getBundle("i18n", Locale.getDefault()); System.out.println(rb.getString("say")); //指定简体中文环境 rb = ResourceBundle.getBundle("i18n", new Locale("zh", "CN")); System.out.println(rb.getString("say")); //通过预设指定简体英文环境 rb = ResourceBundle.getBundle("i18n", Locale.SIMPLIFIED_CHINESE); System.out.println(rb.getString("say")); //指定美国英语 rb = ResourceBundle.getBundle("i18n", Locale.US); System.out.println(rb.getString("say")); //使用自定义的语言环境 Locale locale = new Locale("web", "BASE64"); rb = ResourceBundle.getBundle("i18n", locale); System.out.println(rb.getString("say")); } }按照开发文档的要求: 使用ResourceBundle加载的资源文件都必须放置在根目录 且必须按照${resourceName}_${language}_${region}的方式来命名。这个命名方式正好能对应ResourceBundle::getBundle方法中的参数。例如: ResourceBundle.getBundle("i18n", new Locale("zh", "CN")) "i18n"对应${name} "zh"对应${language} 而“CN”对应$这样我们就可以通过传导参数来使用不同的资源。 如果不指定${language}和${region},该文件就是一个默认文件。 Locale类预设了很多资源类型,比如:Locale.SIMPLIFIED_CHINESE、Locale.US,实际上他们就等价于new Locale("zh", "CN")和new Locale("en", "US")。只是Java的开发人员做了一些静态的预设。 除了预设内容的Locale,我们还可以像Locale locale = new Locale("web", "BASE64")这样添加自定义的内容,他对应名为i18n_web_BASE64.properties的资源文件。 1.1.3 示例2定义三个资源文件,放到src的根目录下面(必须这样,或者你放到自己配置的calsspath下面。 myres.properties bbb=thanks myres_en_US.properties aaa=good bbb=thanks myres_zh_CN.properties aaa=\u597d bbb=\u591a\u8c22 使用 import java.util.Locale; import java.util.ResourceBundle; /** * 国际化资源绑定测试 * * @author leizhimin 2009-7-29 21:17:42 */ public class TestResourceBundle { public static void main(String[] args) { Locale locale1 = new Locale("zh", "CN"); ResourceBundle resb1 = ResourceBundle.getBundle("myres", locale1); System.out.println(resb1.getString("aaa")); ResourceBundle resb2 = ResourceBundle.getBundle("myres", Locale.getDefault()); System.out.println(resb1.getString("aaa")); Locale locale3 = new Locale("en", "US"); ResourceBundle resb3 = ResourceBundle.getBundle("myres", locale3); System.out.println(resb3.getString("aaa")); } }运行结果: 好 好 good Process finished with exit code 0如果使用默认的Locale,那么在英文操作系统上,会选择myres_en_US.properties或myres.properties资源文件。 1.2 LocaleLocale 对象表示了特定的地理、政治和文化地区。 需要 Locale 来执行其任务的操作称为语言环境敏感的操作,它使用 Locale 为用户量身定制信息。例如,显示一个数值就是语言环境敏感的操作,应该根据用户的国家、地区或文化的风俗/传统来格式化该数值。 使用此类中的构造方法来创建 Locale: Locale(String language) Locale(String language, String country) Locale(String language, String country, String variant) 创建完 Locale 后,就可以查询有关其自身的信息。 使用 getCountry 可获取 ISO 国家代码,使用 getLanguage 则获取 ISO 语言代码。 可用使用 getDisplayCountry 来获取适合向用户显示的国家名。 同样,可用使用 getDisplayLanguage 来获取适合向用户显示的语言名。 有趣的是,getDisplayXXX 方法本身是语言环境敏感的,它有两个版本:一个使用默认的语言环境作为参数,另一个则使用指定的语言环境作为参数。 语言参数是一个有效的 ISO 语言代码。这些代码是由 ISO-639 定义的小写两字母代码。在许多网站上都可以找到这些代码的完整列表,如: http://www.loc.gov/standards/iso639-2/englangn.html。 国家参数是一个有效的 ISO 国家代码。这些代码是由 ISO-3166 定义的大写两字母代码。在许多网站上都可以找到这些代码的完整列表,如: http://www.iso.ch/iso/en/prods-services/iso3166ma/02iso-3166-code-lists/list-en1.html。 1.3 native2ascii | 中文资源文件的转码
如果觉得麻烦,可以直接将中文粘贴到里面,回车就可以看到转码后的结果了。
ApplicationContext接口扩展了MessageSource接口,因而提供了消息处理的功能(i18n或国际化)。 与HierarchicalMessageSource一起使用,它还能够处理嵌套的消息,这些是spring提供的处理消息的基本接口。 2.1.2 核心方法让我们快速浏览一下它所定义的方法: String getMessage(String code, Object[] args, String default, Locale loc)用来从MessageSource获取消息的基本方法。如果在指定的locale中没有找到消息,则使用默认的消息。args中的参数将使用标准类库中的MessageFormat来作消息中替换值。 String getMessage(String code, Object[] args, Locale loc)本质上和上一个方法相同,其区别在:没有指定默认值,如果没找到消息,会抛出一个NoSuchMessageException异常。 String getMessage(MessageSourceResolvable resolvable, Locale locale)上面方法中所使用的属性都封装到一个MessageSourceResolvable实现中,而本方法可以指定MessageSourceResolvable实现。 2.1.3 ApplicationContext与MessageSource的工作原理 当一个ApplicationContext被加载时,它会自动在context中查找已定义为MessageSource类型的bean。此bean的名称须为messageSource。 如果找到,则:所有对上述方法的调用将被委托给该bean。 否则,ApplicationContext会在其父类中查找是否含有同名的bean。如果有,就把它作为MessageSource。 如果它最终没有找到任何的消息源,一个空的StaticMessageSource将会被实例化,使它能够接受上述方法的调用。 2.1.4 MessageSource 接口的实现Spring目前提供了两个MessageSource的实现: ResourceBundleMessageSource StaticMessageSource它们都继承NestingMessageSource以便能够处理嵌套的消息。 StaticMessageSource很少被使用,但能以编程方式向消息源(Message Source)添加消息(Message)。 ResourceBundleMessageSource会用得更多一些,为此提供了一下实例化的示例: format exceptions windows 2.1.5 SpringMVC中MessageSource的获取方法 // 资源文件ApplicationResources.properties放在src目录下,也就是classes目录 // 配置文件messages.xml也放在src目录下,也就是classes目录 // 第1种方法 MessageSource resources = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("messages.xml"); String msg = resources.getMessage("XXXXX", new String[] { "OOOOO" }, null); // 第2种方法 ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource; messageSource = new ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource(); messageSource.setBasename("classpath:/ApplicationResources"); messageSource.setUseCodeAsDefaultMessage(true); msg = messageSource.getMessage("XXXXX", new String[] { "OOOOO" }, Locale.CHINA); // 第3种方法 | 此方式中, messageSource Bean 是配置在 spring-servlet.xml 中的 WebApplicationContext wac = RequestContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(request); msg = wac.getMessage("XXXXX", new String[] { "OOOOO" }, Locale.CHINA); 2.2 ResourceBundleMessageSource 2.2.1 概述ResourceBundleMessageSource: 提供国际化的类。 ResourceBundleMessageSource 的底层实现依赖于java.util.ResourceBundle 说的简单点,这个类的作用就是读取资源属性文件(.properties) 然后,根据.properties文件的名称信息(本地化信息),匹配当前系统的国别语言信息(也可以程序指定) 然后,获取相应的properties文件的内容。 2.2.2 配置步骤:示例1ResourceBundleMessageSource的功能就是用Java标准库的ResourceBundle实现的,所以使用起来和ResourceBundle也差不多。 Step1 首先,得将用于处理国际化资源的Bean添加到IoC容器中: @Configuration public class I18nApp { @Bean("messageSource") ResourceBundleMessageSource resourceBundleMessageSource() { ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource(); messageSource.setBasenames(new String[] { "i18n", "extend" });//添加资源名称 return messageSource; } }或 i18n extend切记一定要标记id=messageSource。basenames这个Setter用于指定*.properties资源文件的名称,规则和前面介绍的ResourceBundle一样。 Step2 然后,就可以通过ApplicationContext::getMessage方法获取对应的资源了: @Configuration public class I18nApp { @Bean("messageSource") ResourceBundleMessageSource resourceBundleMessageSource() { ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource(); messageSource.setBasenames(new String[] { "i18n", "extend" }); return messageSource; } public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(I18nApp.class); System.out.println("Spring Default 1:" + context.getMessage("say", null, Locale.getDefault())); System.out.println("Spring Default 2:" + context.getMessage("say", null, null)); System.out.println("Spring Chinese:" + context.getMessage("say", null, Locale.SIMPLIFIED_CHINESE)); System.out.println("Spring Us English:" + context.getMessage("say", null, Locale.US)); System.out.println("Spring Custom:" + context.getMessage("say", null, new Locale("web", "BASE64"))); System.out.println("Spring Argument:" + context.getMessage("info", new String[] {"chkui"},null)); System.out.println("Spring Info:" + context.getMessage("say", null, null)); } } 2.2.2 配置步骤:示例2 Step1 新建国际化资源文件
注意上面的示例代码的这一行: context.getMessage("info", new String[] {"chkui"},null))这里的getMessage向方法传递了一个数组,它用于替换 资源文件中的占位符号。 在例子中我们除了i18n还加载了一个extend.properties文件,文件内容如下: info={0}\u5E05\u7684\u8BA9\u4EBA\u6CA1\u813E\u6C14\u3002文件中的{0}表示这个位置用数组中的[0]位置的元素替换。 还有一点需要注意的是,*.properties文件输入中文等UTF-8的符号时需要保留上面这种ACSII的格式,现在大部分IDE都会自动处理的,切记不要为了方便看内容将*.properties的编码格式切换为UTF-8。 2.4 获取MessageSource接口我们有三种方式获取MessageSource接口: //直接使用 ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(I18nApp.class); context.getMessage("say", null, Locale.getDefault())); //MessageSourceAware(ApplicationContextAware)接口 public class ExtendBean implements MessageSourceAware { @Override public void setMessageSource(MessageSource messageSource) { this.setterMs = messageSource; } } //从容器直接注入 public class ExtendBean implements MessageSourceAware { @Autowired private MessageSource autowiredMs; }需要注意的是,使用@Autowired等方式直接获取MessageSource类型的数据得到的是添加到容器的那个Bean,而其他方式获取到的是ApplicationContext。 X 参考文献 java.util.ResourceBundle使用详解 - 51CTO SpringMVC-ResourceBundleMessageSource使用 - CSDN spring-MessageSource的配置--ResourceBundleMessageSource - CSDN Spring核心——MessageSource实现国际化 - 腾讯云 |
【本文地址】